
Understanding Java Deserialization by Swapneil Kumar Dash Medium
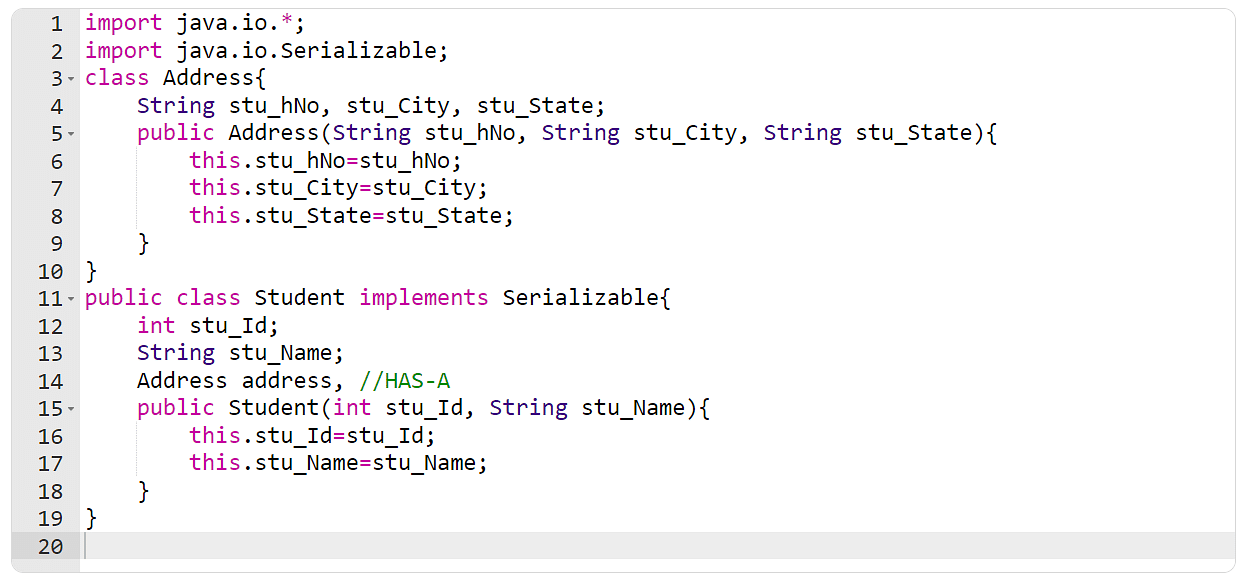
Adding java.io.Serializable - This is equivalent to adding types. There will be no values in the stream for this class so its fields will be initialized to default values. The support for subclassing non-serializable classes requires that the class's super type have a no-arg constructor and the class itself will be initialized to default.
Introduction to Java Serialization [With Easy Examples]
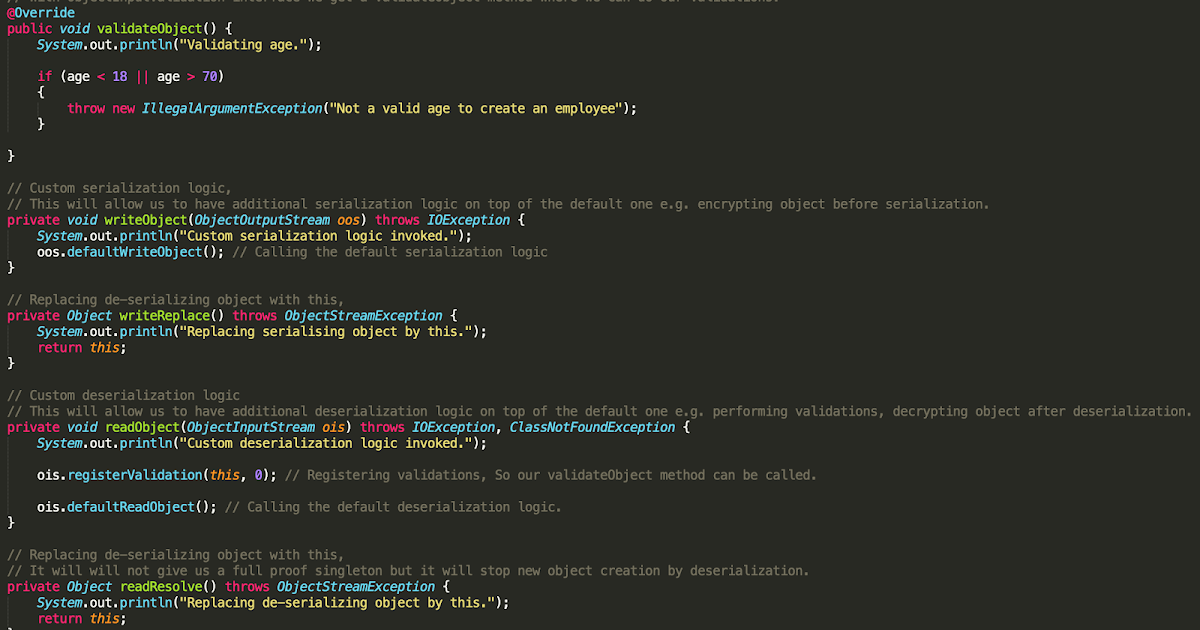
Reading primitive data types is supported by DataInput. The readObjectNoData method is responsible for initializing the state of the object for its particular class in the event that the serialization stream does not list the given class as a superclass of the object being deserialized.
Java Serialization Magic Methods And Their Uses With Example Programming Mitra
Serializability of a class is enabled by the class implementing the java.io.Serializable interface. Classes that do not implement this interface will not have any of their state serialized or deserialized. All subtypes of a serializable class are themselves serializable.

Demystifying Object Serialization in Java
An ArrayList is a re-sizable array in java i.e., unlike an array, the size of an ArrayList can be modified dynamically according to our requirement. Also, the ArrayList class provides many useful methods to perform insertion, deletion, and many other operations on large amounts of data. What is serialization?
How to Serialize Deserialize List of Objects in Java? Java Serialization Example • Crunchify
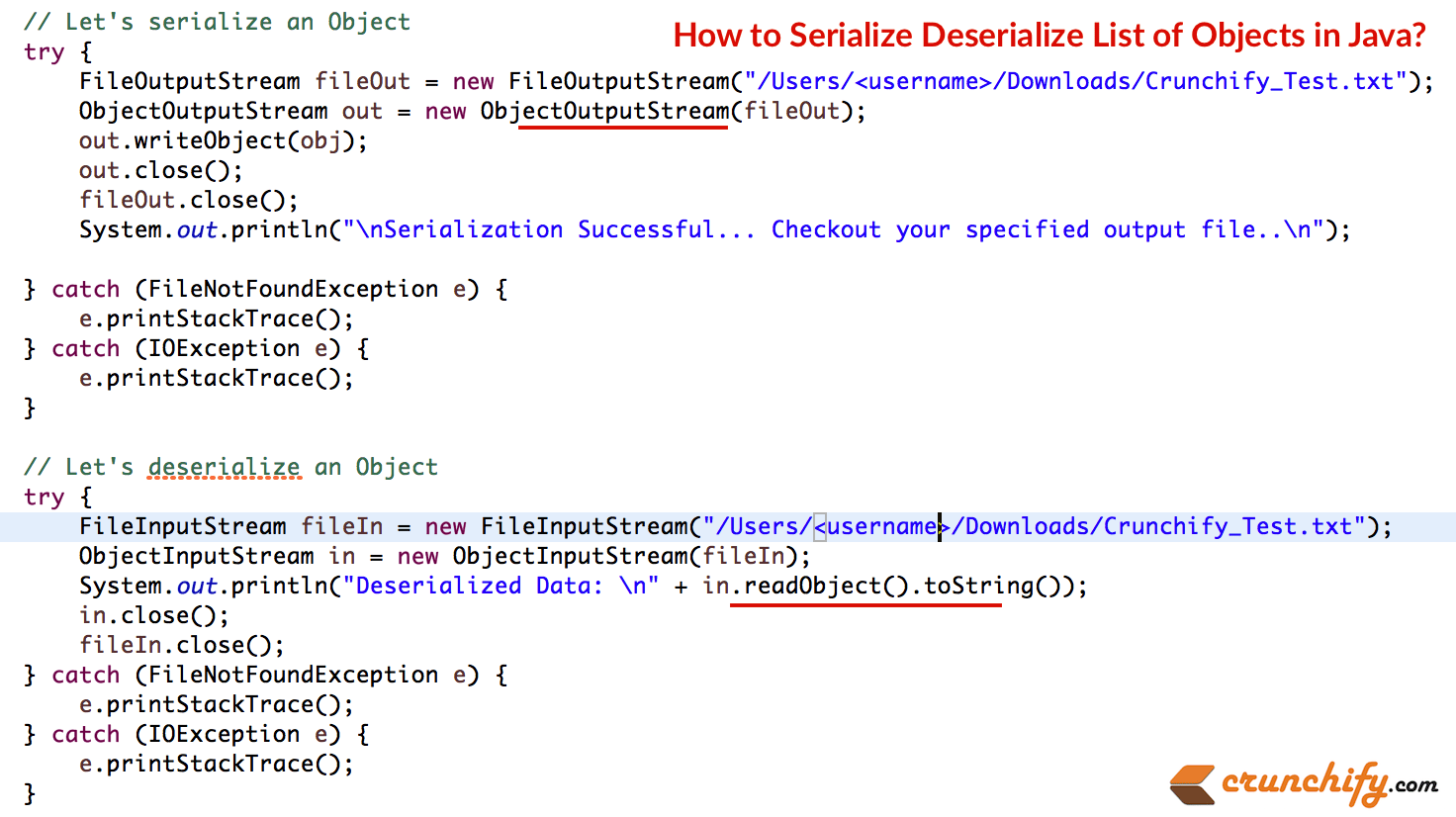
One common use case is to serialize and deserialize a list of POJOs. Consider the class: public class MyClass { private int id; private String name; public MyClass(int id, String name) { this .id = id; this .name = name; } // getters and setters } Copy Here's how we would serialize List
Introduction to Java Serialization [With Easy Examples]
import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectInputStream; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.io.Serializable; public class Product implements Serializable { double Total; String name; double quantity; String unit; double ProductPrice; public Product (String n) { name=n; } private void writeObject (ObjectOutputStream s) throws.

Tutorial 39 Java Serializable YouTube
try { // Serialize data object to a file ObjectOutputStream out = new ObjectOutputStream (new FileOutputStream ("MyData.ser")); out.writeObject (myData); out.close (); // Serialize data object to a byte array ByteArrayOutputStream bos = new ByteArrayOutputStream () ; out = new ObjectOutputStream (bos) ; out.writeObject (myData); out.close ();.

Java Serialization and Deserialization Studytonight
1. Introduction Serialization is the conversion of the state of an object into a byte stream; deserialization does the opposite. Stated differently, serialization is the conversion of a Java object into a static stream (sequence) of bytes, which we can then save to a database or transfer over a network. 2. Serialization and Deserialization

How to Serialize Object in Java Serialization Example
Serialization in Java is a mechanism of writing the state of an object into a byte-stream. It is mainly used in Hibernate, RMI, JPA, EJB and JMS technologies. The reverse operation of serialization is called deserialization where byte-stream is converted into an object.
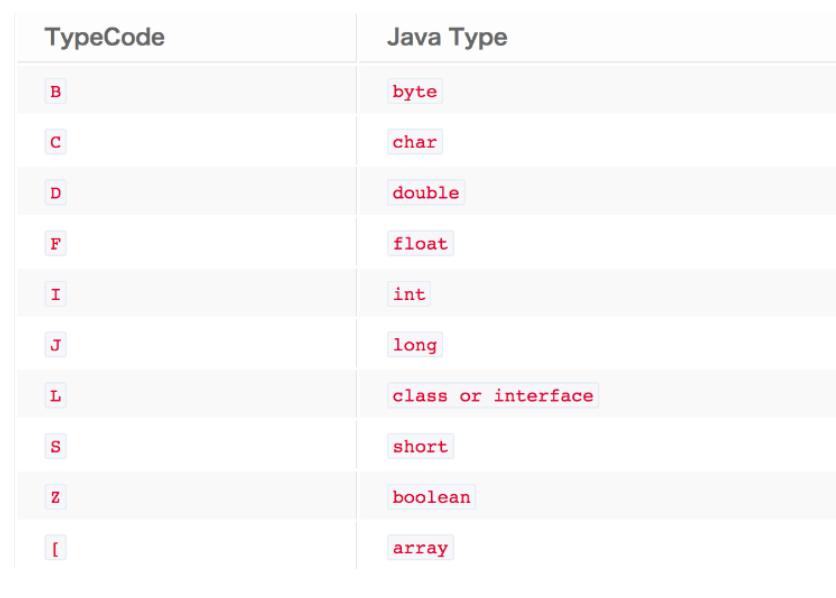
Summary of java serialization
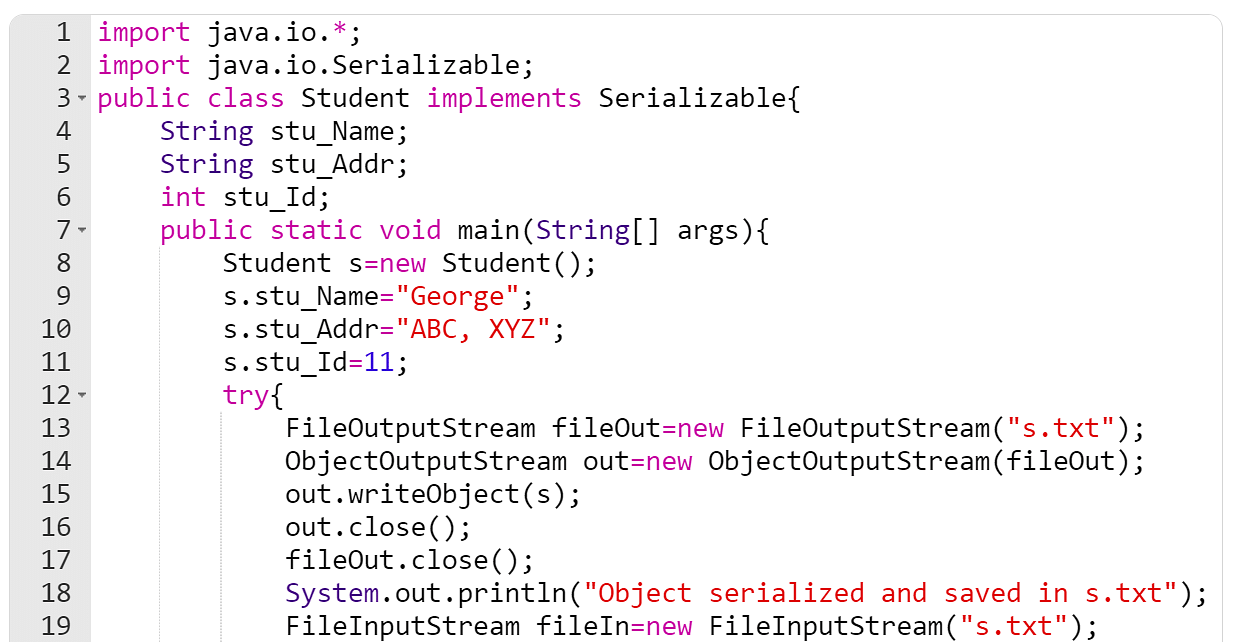
These are the steps: Create Class Item () which implements Serializable. In Main - Create 2 Item Objects. Add it to ArrayList. Serialize the ArrayList. Checkout file to see bytestream of an Object. (Below image) Deserialize the bytestream from the same file to see Object. package com.crunchify.tutorials; import java.io.FileInputStream;

How To Serialize An Object In Java In Database Ui Yuri Shwedoff
Serialization in Java was introduced in JDK 1.1 and it is one of the important feature of Core Java. Serialization in Java. Serialization in Java allows us to convert an Object to stream that we can send over the network or save it as file or store in DB for later usage. Deserialization is the process of converting Object stream to actual Java.

Serialization in Java
Serialization in Java is a powerful tool, but like any tool, it can sometimes cause issues. Let's discuss some common problems you might encounter when working with Java serialization and how to address them. Dealing with Non-Serializable Objects. One common issue is trying to serialize an object that doesn't implement the Serializable.
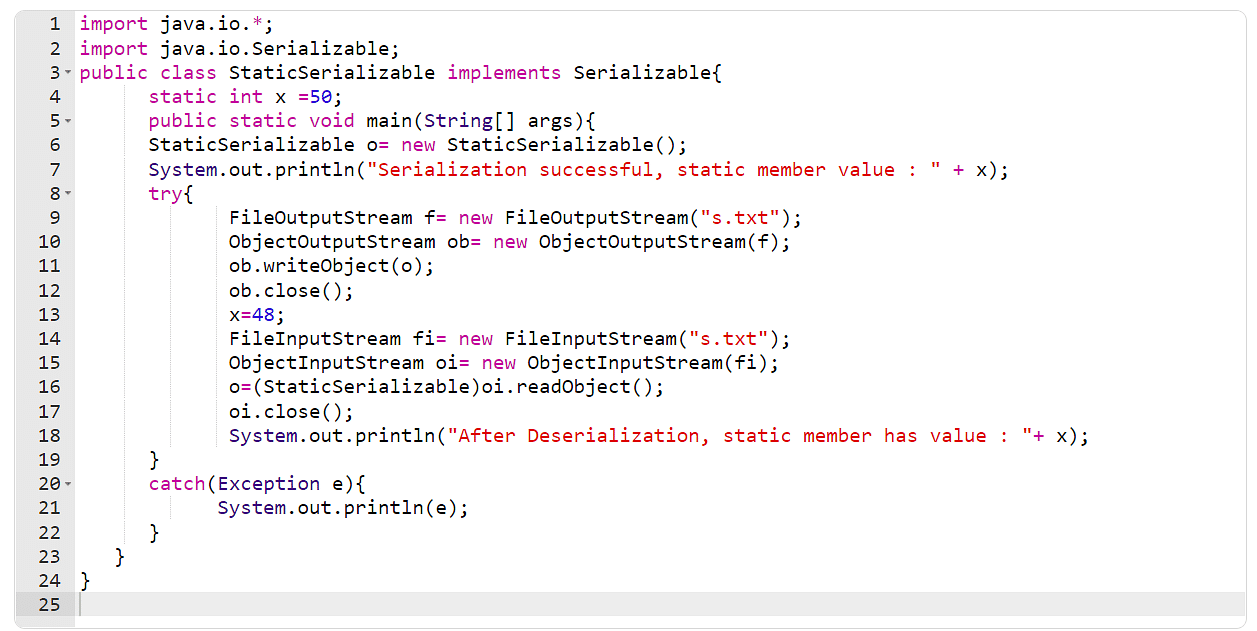
Introduction to Java Serialization [With Easy Examples]
Serialization is a mechanism of converting the state of an object into a byte stream. Serialization is done using ObjectOutputStream. Deserialization is the reverse process where the byte stream is used to recreate the actual Java object in memory. This mechanism is used to persist the object. Deserialization is done using ObjectInputStream.
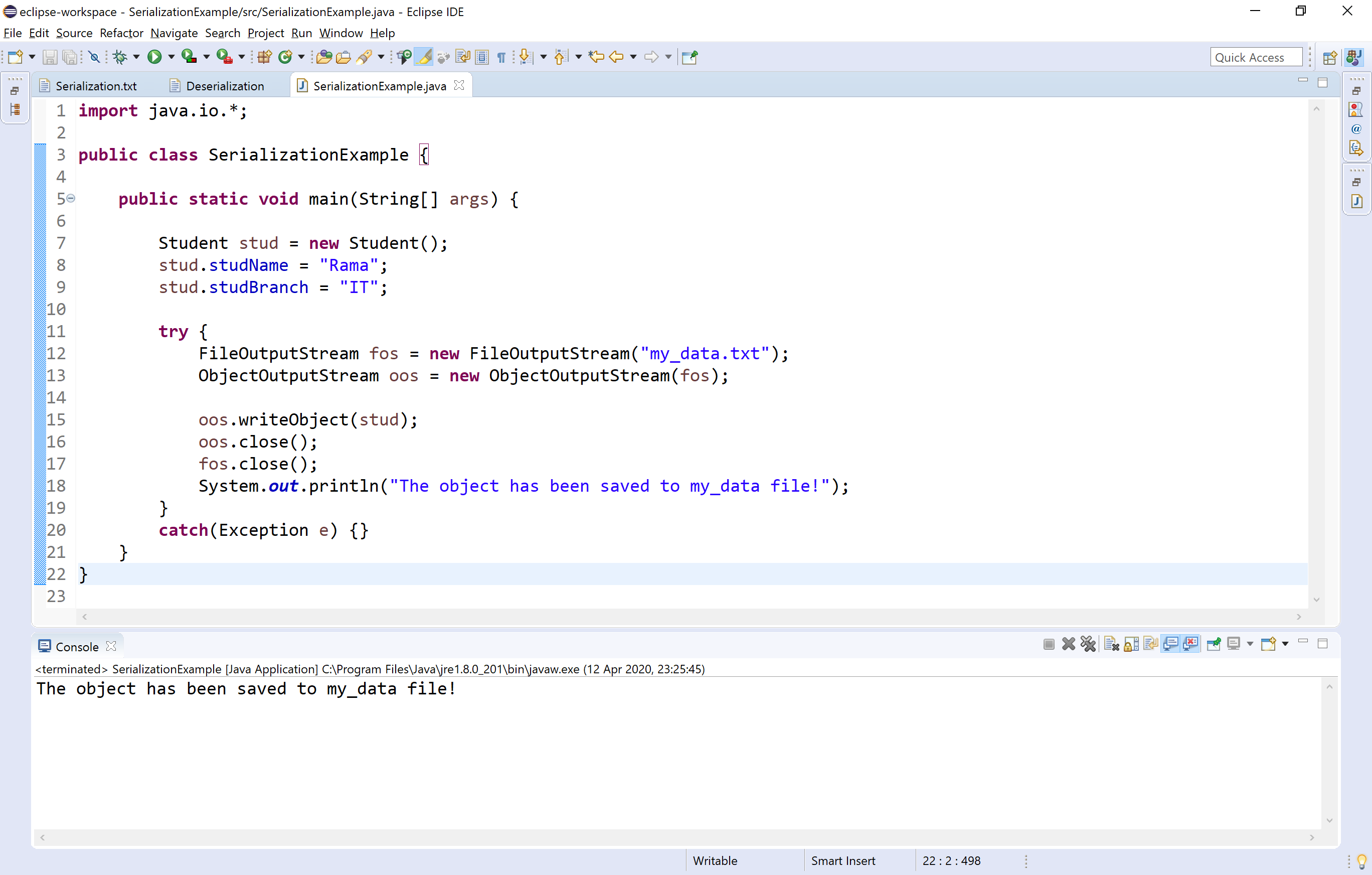
Java Tutorials Serialization and Deserialization in Java
To make a Java object serializable we implement the java.io.Serializable interface. The ObjectOutputStream class contains writeObject () method for serializing an Object. public final void writeObject (Object obj) throws IOException The ObjectInputStream class contains readObject () method for deserializing an object.
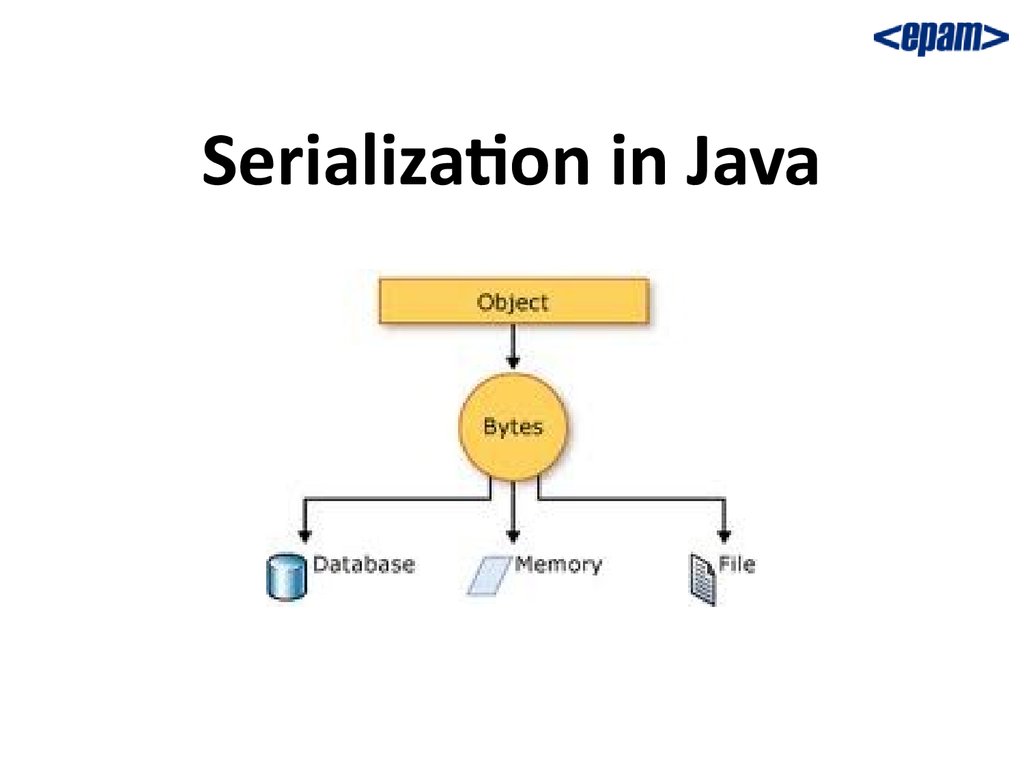
Serialization in Java online presentation
1. Overview Serialization is the process of converting an object into a stream of bytes. That object can then be saved to a database or transferred over a network. The opposite operation, extracting an object from a series of bytes, is deserialization. Their main purpose is to save the state of an object so that we can recreate it when needed.
Introduction to Java Serialization [With Easy Examples]
In this post, you will learn how to Serialize an ArrayList in Java. ArrayList is serializable by default, so we don't need to do anything else except writing the code that will serialize the List into a byte stream. import java.io.FileOutputStream; import java.io.IOException; import java.io.ObjectOutputStream; import java.util.*; class Test.